Nostalgic Kits Central
DC Meter Formulas
Meter Resistance Current Shunt Voltage Multiplier Ohms per Volt
There may be times when a defective panel meter needs repair or replacement. As original meters can be difficult to find, a replacement may have to be made from non-original stock. To help with this process, the following information is provided.
Meter Resistance
To determine the internal resistance of a meter, perform the following steps:
- Connect the meter in series with a DC power source (battery) and a variable resistance R1.
- Starting from highest resistance, vary R1 until you attain a full scale reading.
- Connect a second variable resistor R2 across the meter. Vary R2 untilyou attain a half scale reading.
- After disconnecting R2 from the circuit, measure its resistance. It will be equal to the meter resistance Rm.
Note: Insure that R1 is of high enough a value to prevent allowing too much current to flow through the meter. Use the following formula to estimate a safe value for R1:
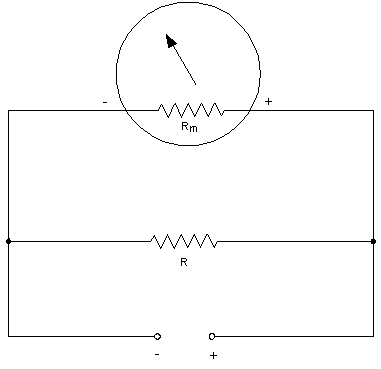
Current Shunt
Use the following formula to calculate the shunt resistance for a current meter:
R = Rm/N - 1
| Where: | R = shunt value in ohms |
| N = new full scale reading divided by original full scale reading |
| Rm = meter resistance in ohms |
Voltage Multiplier
Use the following formula to calculate the series resistance for a volt meter:
| Where: | R = series multiplier value in ohms |
| Efs = full scale reading in volts |
| Ifs = full scale current of meter in amps |
| Rm = meter resistance in ohms |
Ohms per Volt
| Where: | Ifs = full scale current in amps |
Last update: 16 Aug. 2003